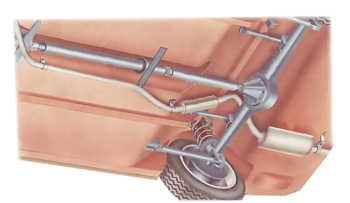
Prises électriques
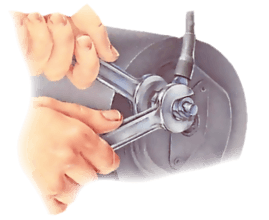
Generally bought in sets, which may vary from about 10 to 56 pieces, socket spanners each have a square drive end that fits into a handle, and a 12-pointed (bi-hex) socket end that fits over a nut or bolt head. A different socket is used for each nut or bolt size.
Socket drives may be 1/4, 3/8, or 1/2in. square, or 3/4in. square for larger sockets. The sockets in a set may be all metric sizes, all imperial, or a mixture. Some sets include a deep 14mm socket for sparkplugs, or they can be bought separately.
A socket set may include a swivelling handle or universal joint, a reversible ratchet handle, a sliding T-bar, an extension bar and a cranked speed brace.
The advantage of sockets and handles is their ability to reach awkward places. They can also be used with a torque wrench. Their use may be limited by the depth of the socket, which may not reach over a long protruding bold, but extra-deep sockets are obtainable.
A socket wrench is a type of wrench that has a socket attached at one end, usually used to turn a fastener.
The most prevalent form is the ratcheting socket wrench, often called a ratchet. A ratchet is a hand tool in which a metal handle is attached to a ratcheting mechanism, which attaches to a socket, which in turn fits onto a type of bolt or nut. Pulled or pushed in one direction, the ratchet loosens or tightens the bolt or nut attached to the socket. Turned the other direction, the ratchet does not turn the socket but allows the ratchet handle to be re-positioned for another turn while staying attached to the bolt or nut. This ratcheting action allows the fastener to be rapidly tightened or loosened in small increments without disconnecting the socket plus socket wrench from the fastener. A switch is built into the ratchet head that allows the user to apply the ratcheting action in either direction, as needed, to tighten or loosen a fastener.
The sockets are attached to the ratchet through a square fitting (called the drive) that contains a spring-loaded ball detent mechanism to keep the sockets or extensions in place. The drive on the ratchet—which comes in standard sizes of 1/4", 3/8", 1/2", 3/4", and 1" (a de facto international standard with no metric equivalents)—allows a wide variety of socket types and sizes to attach to a given ratchet. Some ratchets have quick release buttons on their top for quick socket release. The ratchet handle supplies the mechanical advantage needed by the user to provide the torque needed to loosen or tighten the fastener.
A socket is typically a cylinder which has a female six– or twelve-point recessed opening sized to fit over the common male hexagonal head of a fastener. The opposite end has a standardized square recess to accept the socket wrench's drive size. Male sockets are also produced and are often called bit sockets.
The principal advantage of interchangeable sockets is that, instead of a separate wrench for each of the many different fastener sizes and types, only separate sockets are needed for each size and type. Because of their versatility, nearly all screw and bolt types now have sockets of different types made to fit their bolts or nuts. Sockets often come as a "socket set" with many different sizes or types of sockets to fit the heads of different-sized fasteners. A ratchet of the "set size" is often included with the socket set. Sockets are commonly available in fractional inch and metric sizes, and in short (shallow) and longer (deep) varieties.
Read more on Wikipedia
Cet outil est utilisé dans
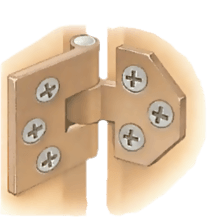
Doors or bonnet and boot lids that do not close properly may have moved out of alignment and nee...
Many hinges are welded to the car bodywork and cannot be adjusted or renewed. But if a door or...
On some overhead camshaft (OHC) engines. the camshaft must be removed to take off the cylinder h...
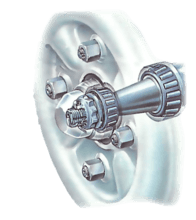
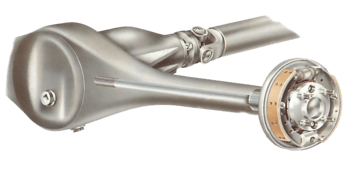
Non-driven wheel bearings - the front-wheel bearings of rear-wheel-drive cars and rear-wheel bea...
Driven wheels - independent suspension Cars with front-wheel drive have front-wheel bearings that...
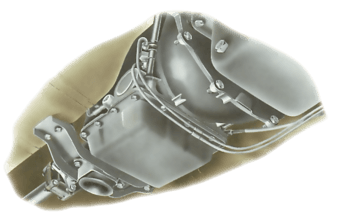
Une transmission automatique nécessite peu d'entretien autre que la vérification régulière du niv...
The rubber anti-vibration mountings of an engine may crack or come away from the metal plates to ...
Brake fluid is generally renewed when a leaking or sticking wheel cylinder on a drum brake is re...
If the oil pump is fitted to the outside of the engine, you may be able to reach it...
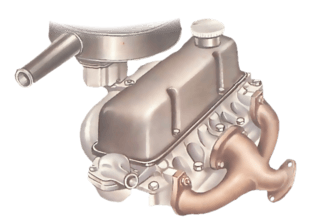
An exhaust-manifold gasket is more likely to need renewing than the gasket on the intake manifold...
Modern telescopic dampers cannot be overhauled at home. The only servicing possible is to replac...
The forces imposed on the anti-roll bar subject it to constant twisting and flexing, which in tu...
Almost all modern cars have hydraulic telescopic dampers in their suspension systems. Where the ...
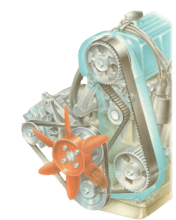
The tension of the toothed belt that drives an overhead camshaft must be checked at the intervals...
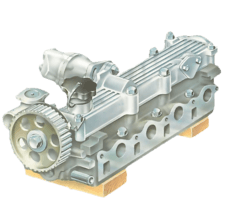
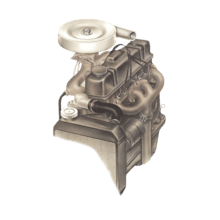
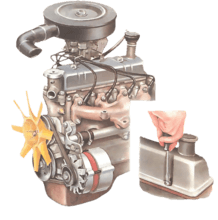
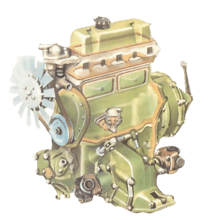
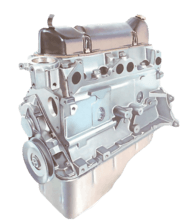
Removing the cylinder head is straightforward on pushrod engines, but more complicated on overhea...
Gaskets and oil seals should be replaced if worn or leaking, or whenever removed during servicin...
Le jeu des soupapes ont des petits espaces entre les sommets des tiges de soupape et la partie d...
Si un moteur à besoin de rajouter de l'huile fraîche plus que d'habitude, ou si vous voyez une f...
Core plugs are also known as expansion plugs, welch plugs and sealing discs - a point to remembe...
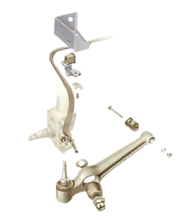
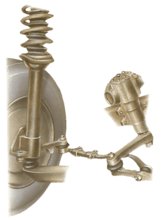
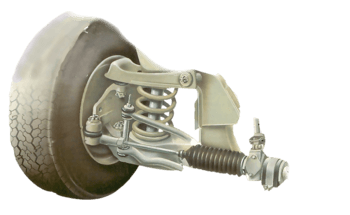
Either or both of the upper and lower swivels may have grease nipples; ball joints have them on ...
A steering box check involves raising the front of the car but keeping its weight on the wheels,...
Vérification de l'essieu arrière et changement d'huile Une fuite d'huile de l'essieu arrière est ...
Wheel bearings need periodic checking - and adjusting if necessary - usually at 12,000 mile serv...
There are two main types of oil seal: static and dynamic. A static oil seal fits between two non...
Half shafts, otherwise known as axle shafts, are fitted in rear-wheel-drive cars only. They give...
Most modern cars have sealed for life joints in at least part of the steering system. These do no...
If testing the starter circuit (See Checking the starter circuit) indicates a fault in the starte...
The timing mechanism in the ignition system causes the sparkplug to fire in each cylinder just b...
A damaged or worn exhaust system allows waste gases from the engine to escape before they have p...
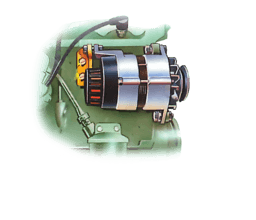
Alternators are powerful enough to cope with the demand for current made by a modern car's electr...