If there is trouble without an obvious cause in any electrical component, test the circuit to find the cause.
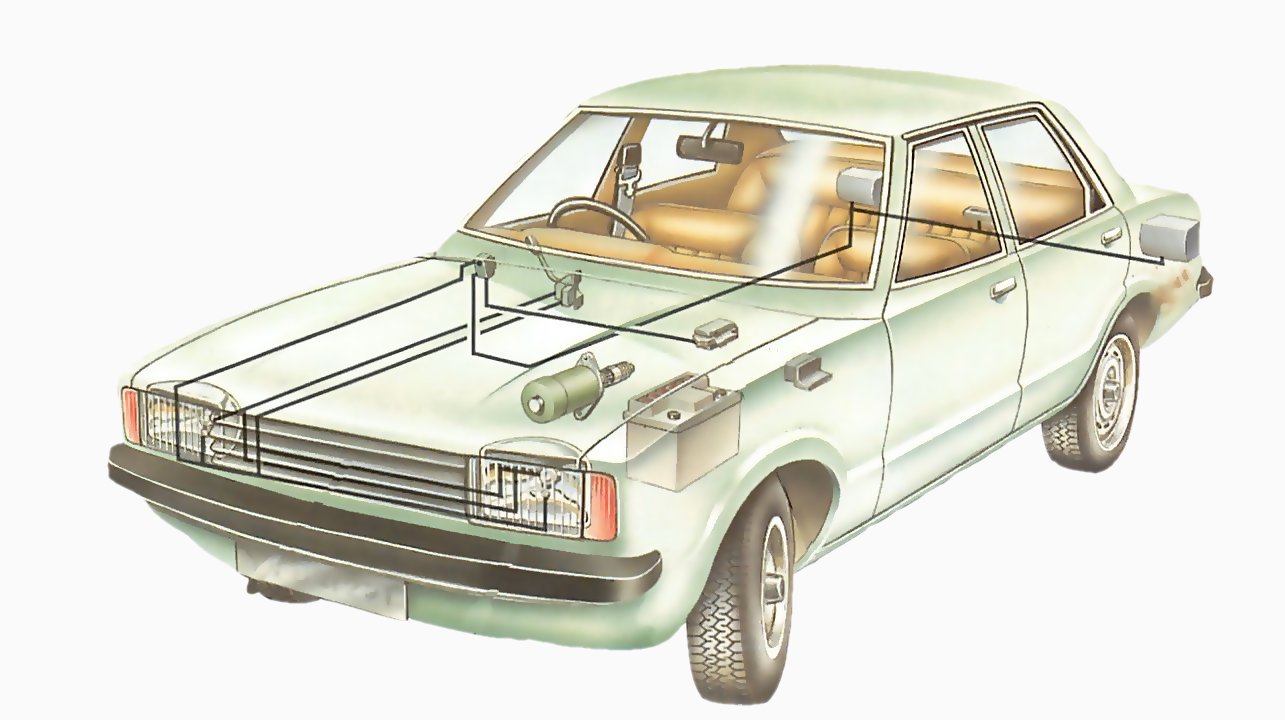
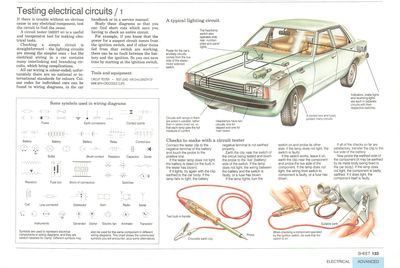
A typical car lighting circuit
A circuit tester is a useful and inexpensive tool for making electrical tests.
Checking a simple circuit is straightforward - the lighting circuits are among the simpler ones - but the electrical wiring in a car contains many interlinking and branching circuits, which bring complications.
This video course is the best way to learn everything about cars.
Three hours of instruction available right now, and many more hours in production.
- 4K HD with full subtitles
- Complete disassembly of a sports car
All car wiring is colour-coded; unfortunately there are no national or international standards for colours. Colour codes for individual cars can be found in wiring diagrams, in the car handbook or in a service manual.
Some symbols used in wiring diagrams
Symbols are used to represent electrical components in wiring diagrams, and they are seldom labelled for clarity. Different symbols may also be used for the same component in different wiring diagrams. This chart shows the most common symbols you will encounter, plus some alternatives.
Study these diagrams so that you can find short cuts which save you having to check an entire circuit.
For example, if you know that the power for a suspect circuit comes from the ignition switch, and if other items fed from that switch are working, there can be no fault between the battery and the ignition. So you can save time by starting at the ignition switch.
How to use a circuit tester
A circuit tester
Connect the tester clip to the negative terminal of the battery and touch the probe to the positive one.
If the tester lamp does not light, the battery is dead (or the bulb in the tester has blown).
If it lights, try again with the clip earthed to the car body: if the lamp fails to light, the battery negative terminal is not earthed properly.
Earth the clip near the switch of the circuit being tested and touch the probe to the 'live' (battery) side of the switch. If the lamp does not light, the wiring between the battery and the switch is faulty, or a fuse has blown.
When checking a component operated
by the ignition switch, be sure that the switch is on.
If the lamp lights, turn the switch on and probe its other
side: if the lamp does not light, the switch is faulty.
If the switch works, leave it on, earth the clip near the component and probe the live side of the component. If the lamp does not light, the wiring from switch to component is faulty, or a fuse has blown.
If all of the checks so far are satisfactory, transfer the clip to the live side of the battery.
Now probe the earthed side of the component (it may be earthed by its metal body being fixed to the car body). If the lamp does not light, the component is badly earthed. If it does light, the component itself is faulty.